|
 |
|
|
|
|
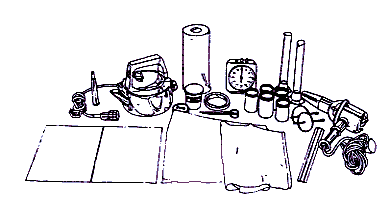
Description:Students determine the best material from which to make a jacket to keep the body warm in a cold, dry, windy climate.This task assesses the student' ability to perform an entire investigation. In this question the independent variable to be tested is the type of the fabric. The dependent variable to be judged is the thermal conductivity of the fabrics. The problem is set outside of the laboratory situation but the pupil is given clues about how to simulate the situation using laboratory apparatus. The apparatus presented to the pupil and its layout are shown in the materials section. This task is designed to take students approximately 30-45 minutes to complete.
Overall Task Content Area:
Specific Knowledge Areas:
Performance Expectations:
National Science Education Standards:8 A SI 1: Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry: Grades 5-81.2 Design and conduct a scientific investigation. Students should develop general abilities, such as systematic observation, making accurate measurements, and identifying and controlling variables. They should also develop the ability to clarify their ideas that are influencing and guiding the inquiry, and to understand how those ideas compare with current scientific knowledge. Students can learn to formulate questions, design investigations, execute investigations, interpret data, use evidence to generate explanations, propose alternative explanations, and critique explanations and procedures. 1.4 Develop descriptions, explanations, predictions, and models using evidence. Students should base their explanation on what they observed, and as they develop cognitive skills, they should be able to differentiate explanation from description providing causes for effects and establishing relationships based on evidence and logical argument. This standards requires a subject knowledge base so the students can effectively conduct investigations, because developing explanations establishes connections between the content of science and the contexts within which students develop new knowledge. 1.7 Communicate scientific procedures and explanations. With practice, students should become competent at communicating experimental methods, following instructions, describing observations, summarizing the results of other groups, and telling other students about investigations and explanations. 8 B PS 3: Transfer of energy: Grades 5-8 (Use the "hot" link on the PALS home page to check the full text of related National Science Education Standards, if desired.) National Council of Teachers of Mathematics:AL1: Understand patterns, relations and
functions: AL3: Use mathematical models to represent
and understand quantitative relationships: PS2: Solve problems that arise in mathematics
and in other contexts:
General Instructions to the Teacher:This task is designed to take students approximately 30-45 minutes to complete. Students will be working individually during this exercise. Students should be ready to work as soon as the period begins.
Materials for "Survival":
Advance Preparation:
Safety:
Extensions/modifications:
|