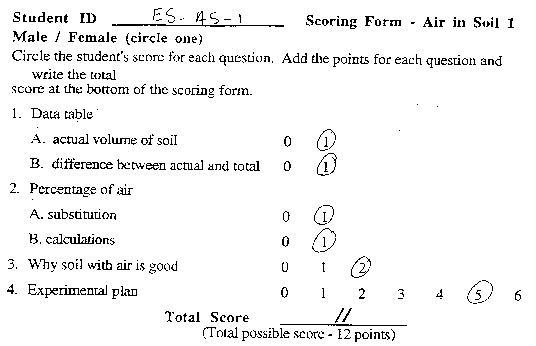
Grade 5-8 Performance Task
Contributed by: New York State Education Department (NYSED)
NYS Alternative Assessment in Science Project (1996)
Student #1
Task:
At this station, you will determine the amount
of air space present in a soil sample.
Materials:
Background:
Soils in the natural environment are a mixture of
mineral particles, plant remains, air, water, and other materials.
Because mineral grains and organic materials are not always regularly
shaped, the particles in soil have spaces between them. These
air spaces may fill with air and/or water.
Directions:
- Pour 100 mL of water into one of the metric cups.
- Place 100 mL of soil into the other metric cup.
- Carefully pour the water into the cup containing the soil,
observing closely as you do so.
- Stir gently until bubbles stop coming from the soil.
- Measure and record the volume of the water and soil mixture
and complete the calculations on the data table.
6. Calculate the percentage of pore space filled
with air in your soil sample. Show your work in the space below.
Percent (%) =
difference between total mixture volume
________________________________ X 100
actual volume of the soil
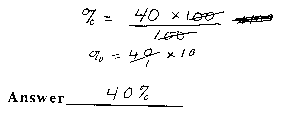
7. Based on your observations in this task, why
might soil with a lot of air or pore space in it be better for
plant growth than soil with little pore space? Use complete sentences
in your explanation.

8. In the space below, design a controlled experiment
you could use to determine the amount of water in soil sample
taken from your backyard.

9. Empty the soil and water mixture into the waste
container and rinse the metric soil cup.

