 |
 |
|
|
|
|
Grades 9-12 Performance Task LABORATORY TEST #1
|
Problem:You will remember that Hooke's Law describes the relationship between the force applied to a spring and its elongation (stretch). That is, if a force stretches a spring, the elongation is directly proportional to the force applied. F = kx Where: F = force in newtons Imagine that you work for a spring manufacturer and your job is to determine whether Sample Spring A will elongate to exactly 0.3 meters when a force of 15 newtons is applied. Your job is to conduct an experiment which will determine whether Sample Spring A meets this specification. |
a) Under the heading PROCEDURE list in order the steps of the procedure you will use to solve the problem. You may include a diagram to help illustrate your plans for the experiment. Include any safety procedures you would follow.
b) Construct a DATA TABLE or indicate any other method that you could use to record the observations and results that will be obtained.
c) At the end of the 30 minutes, your answer sheet for Part A will be collected.
PLEASE NOTE: In Part A, you are NOT to proceed with any part of the actual experiment. You are just to plan and organize a way to investigate the problem.
Materials:
-
a set of masses which totals 1 kg
- Hooke's Law Apparatus (or equivalent)
- graph paper
- Sample Spring A
- C-clamp
- calculator
EXPERIMENT REPORT #1 - Part A
Organize your experiment under the following headings:
PROCEDURE and DATA TABLE
Use the front and back of these sheets if necessary
PROCEDURE
EXPERIMENT REPORT #1 - Part A
DATA TABLE (For results and observations)
Hooke's Law - Part B
Introduction
You will have 50 minutes to complete this part. You have been provided with a detailed Procedure (see next page) which you are to follow. Record your work for Part B on the answer sheet under the appropriate headings.
Problem:You will remember that Hooke's Law describes the relationship between the force applied to a spring and its elongation (stretch). That is, if a force stretches a spring, the elongation is directly proportional to the force applied. F = kx Where: F = force in newtons Imagine that you work for a spring manufacturer and your job is to determine whether Sample Spring A will elongate to exactly 0.3 meters when a force of 15 newtons is applied. Your job is to conduct an experiment which will determine whether Sample Spring A meets this specification. |
a) Perform the experiment by following the steps outlined in the procedure.
b) Under the heading RESULTS/OBSERVATIONS record the data collected in the experiment. Use statements, descriptive paragraphs, and tables of data where appropriate.
c) Under the heading CALCULATIONS show all equations and calculations used.
d) Construct a GRAPH that shows the relationship between the variables measured.
e)Under the heading CONCLUSION give an interpretation of your results.
f) At the end of the 50 minutes, your answer sheets will be collected.
Materials:
- a set of masses which totals 1 kg
- Sample Spring A
- graph paper
- Hooke's Law Apparatus
- C-clamp
- calculator
EXPERIMENT REPORT #1 - Part B
Complete the Procedure as given on these sheets.
Record your Results in the table provided.
Procedure:
- Check the attachment of Sample Spring A and adjust the pointer
to zero on the centimeter scale.
- Attach increasing amounts of mass. Record both the total mass
added and the total elongation of the spring. Use the Data Table
provided.
- Calculate the force of gravity acting on each mass in newtons
(W = mg, g = 9.8 m/sec squared)
- Plot a graph of force against elongation, where the scale
of values for force include 0 to 20 newtons and values for meters
include 0 to 0.4 meters.
- Use the graph to determine the force constant of the spring.
Show all calculations. The slope is:
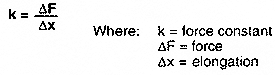
- Determine whether spring A can stretch to exactly 0.3 meters
with a force of 15 newtons applied, by extending the graph through
to force = 15 newtons.
- Report your analysis of this problem under Conclusion.
Observations/Results:
Trial #1Mass (kg)
[1000g = 1kg]Force (N)
W = mgElongation with no load (m)Elongation with load
(m)1020304050607080Record your Calculations, Graph, and Conclusion on these sheets.
Calculations:
Conclusion:
Based on a graphical analysis of the data you collected in this experiment, discuss your conclusion as to whether spring A could stretch to exactly 0.3 meters if a force of 15 newtons is applied. Be certain to explain how you used your data to arrive at this conclusion.